[Article]: Why Choose Injection Molding for Manufacturing?
Injection molding is a dominant manufacturing process used across various industries for its precision, reliability, and versatility. This technique has revolutionized production capabilities by allowing quick and cost-effective fabrication of parts in large volumes. Understanding its integral role in modern manufacturing lays the foundation for exploring its numerous advantages.
What Is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a form of manufacturing that involves injecting molten material into a mold to produce parts with high precision and repeatability. This process can be used with a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, and ceramics, making it incredibly versatile.
-
Melting: The raw material is heated until it melts.
-
Injecting: The molten material is injected into a mold cavity.
-
Cooling: The material cools and solidifies into the shape of the mold.
-
Ejection: The solidified part is ejected from the mold.
Why Choose Injection Molding for Your Manufacturing Needs?
Choosing 3ERP injection molding services provides crucial benefits for competitive manufacturing, including improved efficiency and higher-quality products. From its efficiency in mass production to its ability to produce complex geometries, injection molding is a preferred choice for manufacturers.
Cost Efficiency in Injection Molding
Injection molding significantly reduces labor costs due to its automated nature. The high initial setup costs are offset by the economies of scale, benefiting mass production where unit costs decrease with the number of parts produced.
Speed of Production
The cycle times in injection molding are extremely short compared to other manufacturing processes, often lasting only seconds. This rapid turnaround is crucial in time-sensitive industries where market demands fluctuate rapidly.
Versatility in Materials and Design
Injection molding supports a wide range of materials and allows for the integration of multiple materials into a single component through over-molding or insert molding.
-
Materials: Plastics, metals, and composites can all be used.
-
Design Flexibility: Complex designs can be manufactured with precision, including intricate details and overhangs without additional processing.
Strength and Durability of Molded Parts
The parts produced are strong and durable, with consistent quality across batches. The process also allows for the use of fillers in the injection molds which can enhance strength and thermal stability.
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Injection Molding?
The choice of material impacts the properties of the final product, including its strength, flexibility, and thermal resistance.
Thermoplastics
Commonly used for their ability to be reheated and remolded, making them ideal for recycling.
Thermosetting Polymers
Once cured, these polymers cannot be melted and reshaped, providing enhanced resistance to heat and chemicals.
Elastomers
Offer flexibility and elasticity, ideal for products requiring a soft touch.
Metals (Metal Injection Molding - MIM)
Used for complex, high-strength parts that are difficult to manufacture through traditional metalworking processes.
Ceramics
Provide exceptional heat and corrosion resistance for applications in harsh environments.
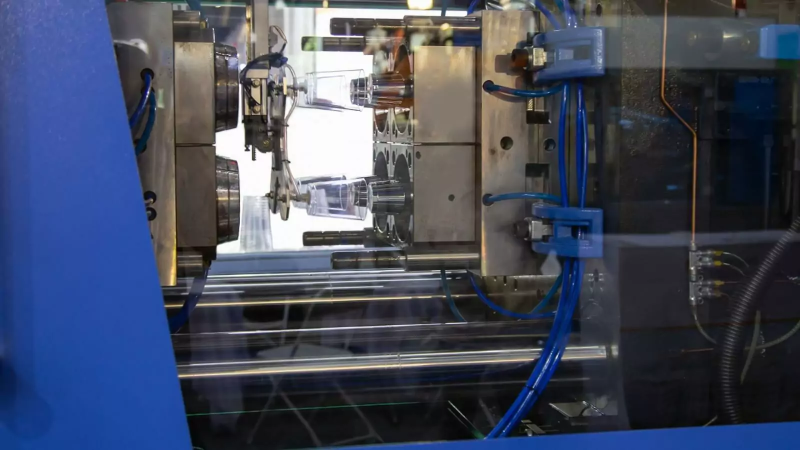
The Injection Molding Machine: An Overview
Understanding the components of an injection molding machine can help in optimizing the manufacturing process.
-
The Injection Unit: Where the material is melted and injected.
-
The Clamping Unit: Holds the mold in place during the injection and cooling.
-
The Mold: The custom-designed part that shapes the molten material.
How to Design for Injection Molding?
Designing for injection molding requires understanding several key factors that influence the quality and manufacturability of the final product.
Wall Thickness Considerations
Uniform wall thickness ensures even cooling and reduces defects like warping or sink marks.
Rib Design
Ribs strengthen parts without increasing wall thickness, but must be designed to minimize stress concentrations.
Gate Location
The point where molten material flows into the mold affects how it fills and must be strategically placed to ensure quality.
Draft Angles
These are critical for easy ejection from the mold, reducing the risk of damage to the part.
Step-by-Step Guide to the Injection Molding Process
From design to production, each step in the injection molding process is crucial for ensuring high-quality output.
-
Mold Design and Creation: The mold is designed and manufactured to meet the specific requirements of the part.
-
Material Selection: Based on the part’s application, appropriate materials are chosen.
-
The Molding Cycle: The actual process of injecting, cooling, and ejecting the part is conducted.
Quality Control in Injection Molding
Maintaining high quality is paramount in injection molding, with several strategies employed to monitor and control the quality of parts produced.
-
Visual Inspection: Checking for cosmetic defects.
-
Dimensional Verification: Ensuring parts meet specified tolerances.
-
Functional Testing: Assessing parts’ performance in intended applications.
Automation in Injection Molding
Automation plays a significant role in modern injection molding, enhancing precision and reducing costs through robotic systems and advanced software.
Benefits of Automation
Increased production speed, consistent part quality, and reduced labor costs are primary benefits of automation in injection molding.
Examples of Automation in Injection Molding
Robotic arms for part removal and assembly lines integrated directly with molding machines are common forms of automation.
Case Studies: Successful Products Made Through Injection Molding
Injection molding is behind many successful products, particularly in sectors like automotive, consumer electronics, and medical devices. These case studies exemplify the process's versatility and efficiency.
Automotive Components
Parts such as dashboards, bumpers, and housing components are commonly produced through injection molding for their durability and complex designs.
Consumer Electronics
Components for devices like smartphones and televisions rely on the precision of injection molding to achieve high-quality finishes and precise fits.
Medical Devices
Injection molding is used for creating sterile, complex components used in medical devices, supporting innovation in healthcare.
What Are the Limitations of Injection Molding?
Despite its many advantages, injection molding does have limitations that can affect its viability for certain applications.
Economic Constraints
The high initial costs for mold design and machine setup can be prohibitive for small runs.
Design Constraints
Certain complex features may be difficult or impossible to mold, requiring additional processing.
Material Limitations
Not all materials are suitable for injection molding; some may degrade or not perform well under the high heat and pressures involved.
Comparing Injection Molding with Other Manufacturing Technologies
Injection molding stands out in many ways when compared to technologies like 3D printing and CNC machining.
-
Speed and Efficiency: Generally faster than 3D printing and more efficient for mass production compared to CNC machining.
-
Strength and Material Diversity: Offers the ability to use stronger materials and more diverse material selections than 3D printing.
Future Trends in Injection Molding
Emerging technologies such as biodegradable plastics and smart molds are setting the path for the future of injection molding, aiming to enhance sustainability and process intelligence.
Biodegradable Plastics
Focus on reducing environmental impact through materials that can degrade naturally without harming the ecosystem.
Smart Molds
Incorporate sensors and feedback systems to optimize the molding process, reduce waste, and increase part quality.
Conclusion
Injection molding remains a cornerstone of manufacturing due to its efficiency, reliability, and broad material compatibility. Whether for mass production or high-precision components, injection molding offers a solution that few other technologies can match, making it a wise choice for manufacturers looking to scale operations and innovate within their industries.












































Interested? Submit your enquiry using the form below:
Only available for registered users. Sign In to your account or register here.