Traceability in Measurement: Standards and Records
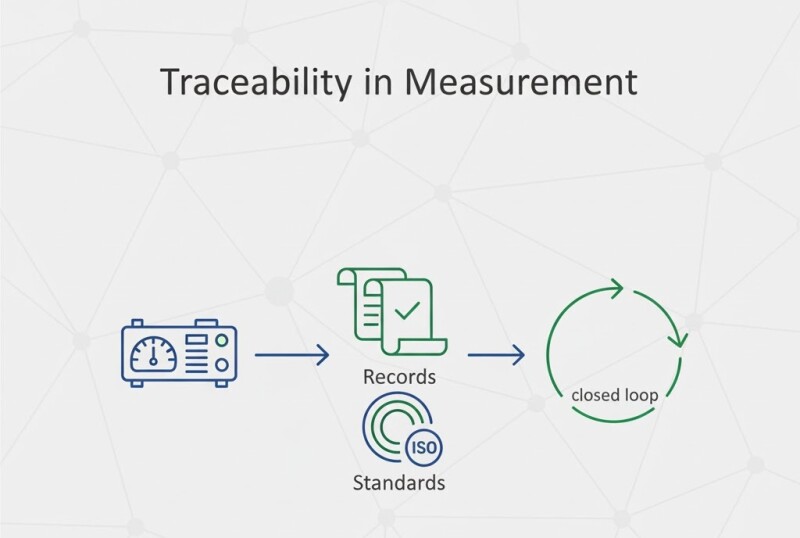
Measurement traceability guarantees that every value on the shop floor can be linked to a recognized standard. In automated systems, maintaining that link requires digital records, calibration hierarchies, and audit-ready documentation.
1. Reference Standards
Each instrument must trace its calibration chain back to a national or international reference (ISO/IEC 17025). Digital calibration hierarchies make this explicit.
2. Electronic Certificates
- Store calibration results in searchable databases.
- Digitally sign and timestamp reports.
- Integrate with quality management systems (QMS) for automatic retrieval.
3. Compliance and Audit Readiness
For regulated industries (pharma, aerospace), traceability extends beyond calibration — covering sensor replacement, configuration changes, and even firmware updates.
Example
A biotech firm digitized 8,000 calibration certificates. Audit prep time fell from 3 days to 30 minutes, with 100% electronic traceability.
Related Articles
- Automating Calibration: Schedules, Sensors, and Sign-Offs
- SPC Meets Metrology: Close the Loop on Quality
- Vision-Based Metrology on the Line: Limits and Wins
Conclusion
Digital traceability ensures confidence and compliance. From gauge blocks to cloud databases, every link in the measurement chain must be documented and verifiable.






































Interested? Submit your enquiry using the form below:
Only available for registered users. Sign In to your account or register here.